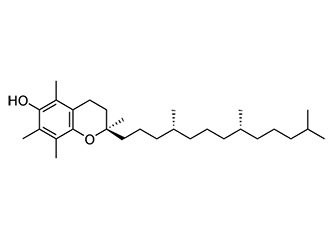
Synonyms
alpha Tocopherol; d-alpha tocopheryl acetate; d-alpha tocopheryl succinate; α-tocopherol; d-α-tocopheryl acetate; d-α-tocopheryl succinate; (2R)-2,5,7,8-Tetramethyl-2-[(4R,8R)-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)]-6-chromanol
Technical Data
CAS Number: 59-02-9 (alpha Tocopherol)
Molecular Formula: C29H50O2 (alpha Tocopherol)
Molecular Weight: 430.71 (alpha Tocopherol)
EC Number: 200-412-2 (alpha Tocopherol)
Natural Vitamin E Oil (1000 IU) USP
| ITEMS | SPECIFICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Description | A Yellow to Yellowish brown, clear and viscous liquid, having a faint characteristic odor. |
| Identification A | Red to orange color development (USP) |
| Identification B | Specific Rotation not less than +24°(USP) |
| Identification C | GC retention time of the major peak(USP) |
| Gardener Index | 4 - 7.5 |
| Acidity | 1.0 ml/g Max (USP) |
| Heavy Metals (as Pb) | 10 ppm Max. |
| Arsenic | 1 ppm Max. |
| Assay | 67.1 % Min. of d-alpha Tocopherol (USP) |
| Residual Solvents | USP<467> only Class 2 Solvents |
| Benzo(a)pyrene | Not more than 1.0 ppb |
Natural Vitamin E Oil (1100 IU) USP
| ITEMS | SPECIFICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Description | Conforms to USP |
| Identification A | Conforms to USP |
| Identification B | +24° Min. |
| Identification C | Conforms to USP |
| Acidity | 1.0 mL/g Max. |
| Heavy Metals | 10 ppm Max. |
| Arsenic | 1 ppm Max. |
| Assay | 80.9 % Min. |
| Organic Volatile Impurities | There is no potential for specific toxic solvents to be present. |
Natural Vitamin E Oil (1300 IU) USP
| ITEMS | SPECIFICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Description | A yellow to yellowish brown, clear and viscous liquid, having a faint characteristic odor |
| Identification (A) | Red to orange color development (USP) |
| Identification (B) | Specific Rotation NLT +24° (USP) |
| Identification (C) | GC Retention time of the major peak (USP) |
| Gardner Index | 5 – 9 |
| Acidity | NMT 1.0 ml/g (USP) |
| Heavy Metals (as Pb) | NMT 10 ppm |
| Arsenic | NMT 1 ppm |
| Assay | NLT 87.3% of d-α-Tocopherol (USP) |
| Benzo (a) Pyrene | NMT 1.0 ppb |
| Residual Solvents | USP <467> only class 2 solvents within limit |